Workshop - Electrical System
Wiring Diagrams for Various Models
Lambretta Li 175 Series 1 and 2
This information and the pictures included are provided from the 'Instructions for Repair Shops' for these models published in 1963. It is intended for informational purposes and we would recommend seeking professional advice before undertaking anything described in the Workshop section.
Electrical Equipment

175/1i - First series (fig. 61 below)
The electric circuit is fed by a flywheel magneto of 40 W power, which supplies current to the H.T. Coil for engine ignition and with the control switch at 3, feeds the side parking lights (6 V 1.5 W), the rear number plate bulb (the 6 V - 3W filament of the dual 6 V - 3/20W bulb), the speedo bulb and the headlamp bulb.
Further through a rectifier it charges the battery (6 V 200 AH), which when the switch is in position 2, feeds the rear number plate bulb and the city light bulb in the headlamp. It also feeds independently to the position of the switch, the horn, the 'flasher unit and the stop light ( this being the 6 V - 20 W filament of the dual 6 V - 3/20 W bulb).
The main control switch situated on the instrument panel has five positions :
| Position 0 | Key straight and all lights out and dead engine. |
| Position ST | Key rotated to the Left - Pilot light in the headlamp, number plate light, side parking lights - dead engine. (For parking in non-illuminated districts). |
| Position 1 | Key rotated to the Right - 1st click all lights out. (Day driving). |
| Position 2 | Key rotated to the Right - 2nd click, City light in the headlamp - number plate light, side lights and speedo light (extra) on (For night city driving). |
| Position 3 | Key rotated to the Right - 3rd click, Headlamp, rear light, side lights and speedo light on. (Night driving in country). |

The electrical windscreen wiper (extra) if fitted is fed directly from the battery through a fuse.
The rectifier impedence group, the fuse group, the flasher unit and the junction box are grouped on a panel placed under the left hand side of the dashboard (See fig. 62).
To reach the fuses, unscrew the serrated button on the box placed under the dashboard.
The four fuses protect the following circuits:
- First from the left: Parking lights, rear number plate light and speedo light.
- Second from the left: Flasher indicators
- Third from the left: Stop light
- Fourth from the left: Battery charge
Two warning bulbs are placed on the instrument panel ;
Green = City Lights.
Orange = Flasher indicators.
The flasher indicator, headlamp beam control lever together with the horn button are incorporated in the switch fitted on the right hand handlebar grip.
 |
 |
 |
Wiring Diagram (Figure 61) |
Equipment and Part Numbers |
Bulbs |
175/li - Second Series (Fig. 64) ( 4 Poles Flywheel Magneto)
The electrical circuit is fed by the 12 V 18 Ah battery.
The flywheel magneto, 50 W, feeds the battery through a regulator rectifier group.
The cable (grey) from the rectifier group carries current to the main switch (placed on the left hand side of the instrument panel), for feeding all the circuits connected or dependent on the switch, while through a fuse, gives current direct to the hydraulic brake stop light switch and horn. These are the only two circuits not connected to the main switch.
The main switch has 5 positions:
| Position 0 | Key straight - All lights out. Engine still. |
| Position ST | City lights, speedo light, parking and rear number plate lights on. Engine still. (For parking in non-illuminated areas). |
| Position 1 | Key turned to Right - 1st. click. All lights out - Normal day driving. |
| Position 2 | Key turned to Right - 2nd. click. Side lights, rear lights and number plate light on, (For night driving out of town). |
| Position 3 | Key turned to Right - 3rd. click. Headlamp, side lights ear and number plate lights on. (For night driving out for town). |
The Key can only be extracted from switch when in positions 0 or ST.
The flasher indicator, headlamp beam, and horn controls are grouped on the switch fitted on the right hand side of the handlebar.
The regulator-rectifier group is fixed to the left hand cabin upright over the battery. A 15 A fuse contained in the rectifier group protects the charging circuit. On the hinged dashboard panel, around the main switch three warning lights are fitted:
- over the switch - an Orange flasher indicator light.
- to the left of the switch - a Red ignition warning light. (This should light up when engine is still and key is in the main switch, or with engine idling, It should go out when vehicle is running).
- To the right of the switch - a Green parking warning light.
On the inside of the panel, (which is reached by lifting the panel) are fitted the following:
- Fixed junction box complete with fuses.
- Flasher control unit
- Warning lights bulb holders.
The five fuses protect the following circuits:
- Rear stop lights and horn,
- Trafficators (orange warning light) and windscreen wiper (extra).
- Headlamp bulb.
- Front side lights (green warning light).
Rear parking and speedometer lights (extra).
NOTE - To avoid serious damage to the regulator group, the engine must not, under any circumstances, be started if the battery is not connected.
 |
 |
 |
Wiring Diagram (Figure 64) |
Equipment and Part Numbers |
Bulbs |
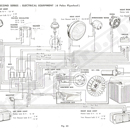
175/Li - Second Series (Fig. 65) ( 6 Poles Flywheel Magneto)
The electrical circuit is fed by the 12 V 18 Ah battery.
The 6 Pole flywheel magneto of 80W output charges the battery through a rectifier. The five coils in the flywheel are connected in series with two (yellow) wires and an intermediate wire. (Red)
A 15 amp, fuse is inserted in the battery charging circuit and is located in the junction box placed under the seat support beam. To reach the fuse, remove plastic cover on box.
The current is distributed through the regulator to direct usage circuits (hydraulic stop light switch and horn) and the main switch.
The main switch Key has 5 positions:
| Position 0 | Key straight - all lights out - engine still, |
| Position ST | Key turned to the left: city, speedo (extra), rear parking and number plate lights ON. Engine still, (Parking in dark areas). |
| Position 1 | Key turned to the right - 1st click. All lights out. |
| Position 2 | Key turned to right - 2nd click. Front side, rear parking and number plate light ON. (Night driving in town). |
| Position 3 | Key turned to the right, - 3rd click. Headlamp front side, rear and number plate lights ON. (Night driving out of town). |
The switch key can only be released when in position 0 or ST.
The flasher indicator, headlamp and horn, controls are incorporated in the switch fitted to the right hand side of the handlebar.
The regulator group is fixed to the left hand cabin upright over the battery.
The warning fights are situated on the hinged instrument panel on the dashboard as follows:
- Over the main switch - ORANGE Flasher indicator warning light.
- To the left of the switch - RED ignition warning light (this remains on when engine is running as it is in the ignition circuit).
- To the right of the switch - GREEN parking bulbs warning light.
The following items are located on the inside of the instrument panel and can be reached by lifting the panel:
- Junction Box complete with five fuses 8 amp each
- Flasher control unit
- Warning light bulbholders
- Spare fuse 8 amp
The five fuses protect the following circuits:
- Rear stop lights and horn
- Flasher indicators and windscheen wiper (extra)
- Headlamp beams
- Front side lights and green warning light
- Rear parking lights and speedo bulb (extra)
Note: To avoid damage to the regulator group the engine must not be started unless the battery is connected
 |
 |
 |
Wiring Diagram (Figure 65) |
Equipment and Part Numbers |
Bulbs |
Instructions for Battery Use and Maintenance (FOR INFORMATION ONLY)
| 157 | Preparation of acid and checking. The acid to be used is Sulphuric Acid diluted in distilled water to a density of 1.26 and 1.27 grams/cc (30"-31" Beaume). The acid to the correct density is easily available. Before proceeding to the battery filling it is necessary to check the density of the acid therein with a hydrometer. The acid should be kept in glass containers and handled with care. To make the mixture, add the sulphuric acid slowly to a basin of distilled water, mixing continuously. Never pour water into the acid, otherwise it will cause a spray of strong caustic drops. To reach the correct dilution, providing the acid has a density of 1.83 gr/cc. use 1 part acid to 2.8 parts of distilled water. As heat is generated by the mixing, leave to cool, check density, correcting with small additions of water or acid. |
| 158 | Refilling. Remove the caps on each cell and fill up until liquid level is about Al over the top edge of the cell separators. |
| 159 | Recharge. Having refilled the battery as above, it can be used right away, but it is generally advisable to give it a refresher charge of about 3 to 4 hours. This charge should be about 1/10 of the battery capacity. (example - if the battery is of 18 Ah. the charge, should be of about 1.8 to 2 Amps). After the charge shake the battery to eliminate gas bubbles, top up with distilled water, close the cell plugs securely, and wipe any trace of acid from the outside. |
Electrical Circuit Checking Operations
Instruments required:
- Rev. Counter - 0 to 6000 R.P.N.
- Voltmeter for DC - 0 to 10B.
- Amperometer for DC - 0 to 3 A.
- Milliamperometer for DC - 0 to 0MA.
- Hydrometer for battery liquid control,
- Wiring circuit tester - A megohmeter is recommended.
Adjustment of the Headlight

| 160 | Check tyre pressures. |
| 161 | Place a screen in front of the vehicle as shown in Fig. 66. |
| 162 | Place the vehicle in normal load conditions. |
| 163 | Loosen the rear headlamp screw V and rotate lamp until the upper edge of the zone illuminated by the dipped ray coincides with the horizontal line drawn on the screen. |
Battery Checking and Maintenance - INFORMATION ONLY
Never allow the battery to remain in a discharged or low state of charge for any lengthy period, otherwise damage to the plates may occur. Measure the density of the liquid by means of a hydrometer. A density of 1.28 g/cm3 (equal to 32° Beaume) corresponds to a fully charged battery, while a density of 1,21 q/cm3/ ( 25"Be ) indicates that the battery needs urgently recharging to avoid corrosion of the plates. Should lower densities be found, then it is advisable to send the battery to the makers, because the process of corrosion has already set in.
Check level every month or as required, add distilled water until the level is about 1/4" above the cell separators. It is advisable to add the distilled water after and not before a journey.
Check at regular intervals to see if the battery terminals are well tightened to the cables and greased with vase- line to avoid corrosion.
Should the machine be laid up for a considerable time, it is advisable to remove the battery, store in a dry place
at normal temperature and arrange for a monthly recharge to maintain efficiency.
On refitting the battery to the machine, great care must be taken in connecting the battery in the correct way. Positive pole (+) connected to machine circuit cable - Negative pole (—) connected to earth screw on battery carrier.
Carry out recharging of the battery only on D.C. or rectified current having an intensity equal to 1/10th of its capacity (1.8 to 2A). Check each cell with a voltmeter, when the voltage registers 5.7 V (1st Series 175 Ii) and 11.4 V ( 2nd series 175 Ii) continue charge for a further 3 hours.
After charging, shake the battery to allow the exit of the gas formed during charging, then bring the level of the liquid to the height mentioned above.
Checking Absorption - Charging Circuit - Inverse Current
| 164 | Circuit current absorption check |
||||||||||||
| 165 | Checking battery charging circuit.
Should the current measured be lower than the prescribed value, this could be caused by : - faulty rectifier - in this case replace. |
||||||||||||
| 166 | Inverse current check To carry out a reading, the main switch key should be in the « OFF » position i.e. Vertical « 0 ». Connect positive terminal of the milliammeter to the positive terminal on the battery and the negative terminal of the meter to the cable from the main circuit to the battery (See fig. 67 for 175 Ii - 1st series and fig. 68-68 bis for 175 Ii - 2nd series). |
PLEASE NOTE THIS SECTION STILL HAS INFORMATION TO BE ADDED - COMMENT DATED 16th APRIL 2013











